
- Emailenquiry@trainingmithra.com
- Enquiries +918269258269


Table of Content
Sensing the physical phenomena is a key aspect in any Internet of Things application and sensors help exactly to do the same.
Sensors:
Both sensors and actuators are collectively called ‘Transducers’. Transducers are the devices that convert the energy of one kind into the energy of another kind. Some common transducers are as follows:
| Quality Being Measured | The input device (Sensors) | Output device (Actuators) |
|---|---|---|
|
Light |
Light Dependent Resistor (LDR) Photo Diode Phototransistor Solar cell |
Lights and Lamps LEDs and Displays Fibre Optics |
|
Temperature |
Thermocouple Thermistor Thermostat Resistive Temperature Detectors (RTD) |
Heater Fan |
|
Force or Pressure |
Strain Gauge Pressure switch Load cells |
Lifts and Jacks Electromagnetic vibrations |
|
Position |
Potentiometer Encoders Reflective/slotted opto-switch LVDT |
Motor Solenoid Panel Meters |
|
Speed |
Tacho – generator Reflective/slotted optocoupler Doppler effect sensors |
AC and DC Motors Stepper Motor Brake |
|
Sound |
Carbon microphone Piezoelectric crystal |
Bell Buzzer Loudspeaker |
A sensor is a transducer that converts a physical phenomenon into an electrical signal. Sensors provide the interface to the physical world through electrical devices, such as microcontrollers/microprocessors, computers, etc. Sensors may have multiple transducers. For example, for a sensor that has to convert something in the form of chemical energy into electrical energy, if it is difficult to convert directly from chemical to electrical energy, it uses more than one transducer. Transducer 1 will convert chemical energy to heat and transducer 2 will convert heat to electrical energy.
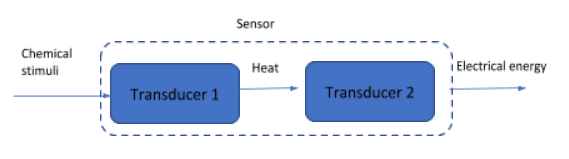
There are many types of Sensors and they are classified based on output type, method of detection, means of detection, conversion phenomenon, active or passive, etc., and with the advent of the Internet of Things, these sensors have undergone evolution and as a result of that today we have ‘Smart Sensors‘, where we are integrating electronics into a sensor to make it an intelligent sensor.
What is a Smart Sensor?
A sensor producing an electrical output when combined with interfacing electronic circuits is known as “Smart Sensor", it is a combination of both sensor and actuator.
The smart sensor will have intelligent features and some electronics that can perform:
Sensor + interfacing circuit = smart sensor
Smart Sensor Functional Diagram:
A Smart sensor senses measurand - physical quantity, property or Condition to be measured and Signal condition and storage unit has Analog to Digital converters which converts the signal into a digitally readable form and stores in its memory and further processes it like aggregating, error checking, etc., before sending to microprocessor or microcontroller.
Click here to Learn Data Science Training in Chennai

Smart Sensor Functions:
Smart sensor carries four functionalities
Measurement is a common functionality of any sensor where the sensor is expected to detect a physical signal and convert the signal into an electrical signal. Signal will also do some signal processing if it is an integrated sensor. Smart sensors have additional features like Correction compensation. Let us consider an example of correction compensation – Offset (An offset means that the sensor output is higher or lower than the ideal output.)and gain (Gain is a ratio between input and output) are two parameters of sensors mostly adjusted during fabrication and calibration cycle (Sensor calibration is a method of improving sensor performance by removing structural errors in the sensor outputs) are done in the factory itself, based on that adjustment in offset and gain is done. These adjustments usually change in time for different reasons, requiring the device to be recalibrated. Smart sensors may have the correction functions in its memory and processors may apply for compensation from time to time that means they would be able to do Self-calibration.
Diagnosis - This is the inherent ability for a smart sensor to determine if it operates properly. With the IoT system complexity steadily increasing, malfunctioning components must be identified as quickly as possible.
The configuration in terms of technological, functional, operational aspects include Active Installation Support - sensor would be able to alert on alignment errors or installation errors
The verification function may offer services, such as continuous supervision of the intelligent sensor’s behaviour, using a set of supervisory equipment/circuits implemented in the sensor. Supervisory results can be stored in a database (eg: FIFO, Flash) & systematically updated and available for maintenance purposes. It offers the necessary services for diagnosis, allowing the user to locate faults whenever they are detected.
Another important feature of the smart sensor is communication and this is a bidirectional – sensor to the main microprocessor or microcontroller and vice versa. Smart sensors will have mechanisms for synchronization communication between sensors and microcontrollers and they will support different data rates. Industrial Smart sensors come with a plug and play mechanism, like a CAN bus mechanism where they can be connected to the network and removed as easily as possible and also mechanisms to identify their own identity in the network.
Smart Sensors Networks/ Wireless Sensor Networks
Many high-end applications are designed by integrating IoT connectivity into Smart sensor technology. We are calling such connected Smart sensors as Smart Wireless Sensor networks or WSNs. These WSNs will sense, measure and collect information from their environment or from the object (that has to be measured) and they transmit to the outside world based on a user-defined decision process.
Some examples of Wireless Sensor nodes or Smart sensor nodes:

In the future, we may expect smart sensors which Modify their behaviour to optimize the collection of data from the external world along with advanced learning capabilities like machine learning that Combines -
These sensors understand the environment they are put into and they can manage a wide range of conditions using their functional features like auto-calibration - these calibrate themselves without any further connections, compensated measurements that is they will compensate errors in the measurements and also, they evaluate their own health.
Smart Sensors have their own components integrated onto the same PCB (Printed Board Circuit) by using these Smart sensors one can reduce production testing costs since they have firmware-based signal processing capabilities, processed data validation, power management, and multi-sensing capabilities. This results in improved reliability and performance.
Smart Sensors Networks Applications

21 May 2022

21 May 2022

21 May 2022

20 May 2022

20 May 2022
31 Dec 2021

24 Dec 2021

24 Dec 2021